Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of primary liver cancer, typically occurring in individuals with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. It is a serious and life-threatening condition, but early detection and appropriate treatment can improve outcomes.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is primarily associated with underlying liver disease and chronic conditions.
The main risk factors include chronic hepatitis B and C infections, cirrhosis, excessive alcohol, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, aflatoxin (a toxin found in contaminated food products), and genetic and metabolic disorders.
Liver Transplant
Karolinska University Hospital runs one of the more extensive liver surgery units in the Nordics, and has a special assignment for liver transplants on behalf of the Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare. Both children and adults undergo transplants with excellent results at Karolinska. Liver Transplant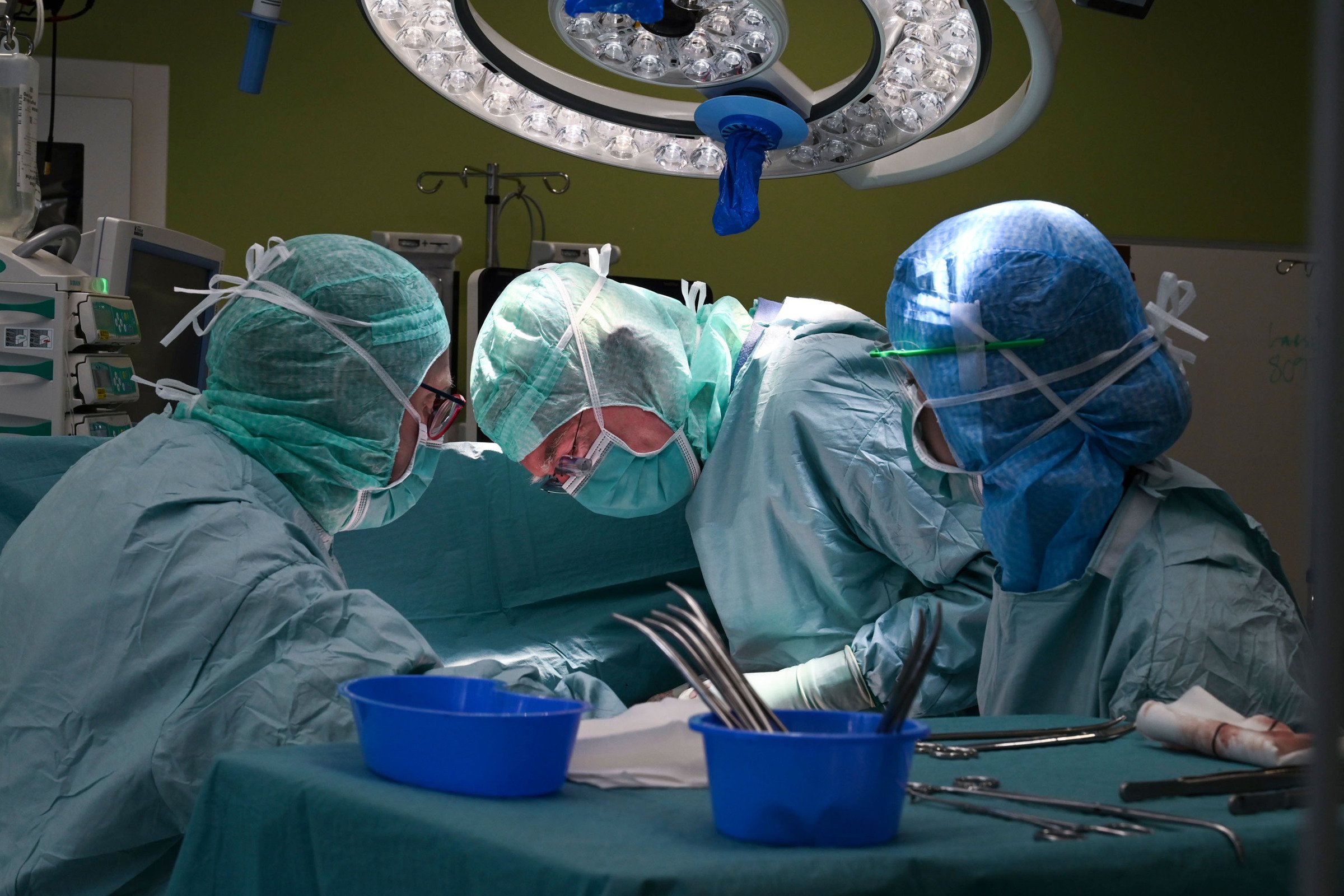
Center
We aim to significantly improve the quality of life for a vast number of patients with various diseases, as well as give new life to those for whom there is no other treatment.